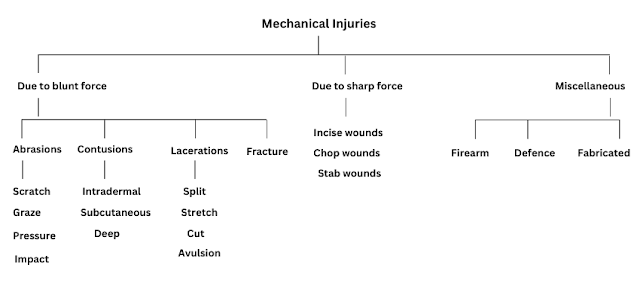
Classification of Thermal Injuries
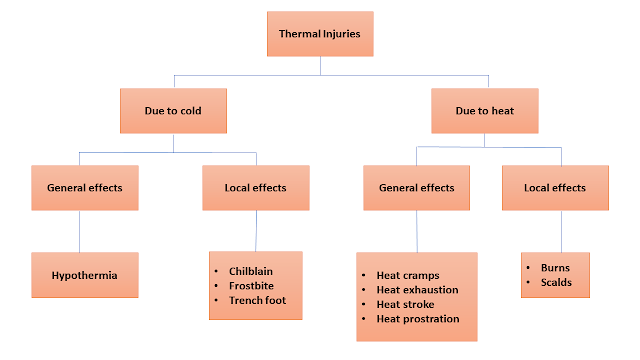
A) Cold Injuries 1. General Effects 1. Hypothermia Exposure of the body to cold, below temperature 35 ℃ (95 ℉) is called Hypothermia. When the temperature of the body falls below 32 ℃ to 24 ℃ , there is disorientation, loss of consciousness, loss of reflex, and a fall in respiration heart rate, and blood pressure. Red patches and pallor of the skin, edema of the face, and stiffness of neck muscle may be seen. Postmortem Findings 1. External Patches of pink/brownish-pink discoloration on the skin. Edema on feet and blistering of skin can be seen. The extremities may be white (White deaths) 2. Internal Lungs are congested and show hemorrhages. The heart shows dilation of the right atrium and ventricle. Wischnewslay spots may be seen in the stomach. Fatty changes in the liver and contracted spleen. Hemorrhages in core muscle. Ulceration of the colon. 2. Local Effects 1. Chilblain These are red, itching, and skin lesions due to exposure to cold. They may be associated with edema and ...