Life Cycle of Vulnerability Management
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is a program that addresses common cybersecurity weaknesses in an organization's software, hardware, and network. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers to steal data or do a brute-force attack.
Therefore, vulnerability management helps to identify, close, and track these types of vulnerabilities and prioritize them in order of high risk to low risk.
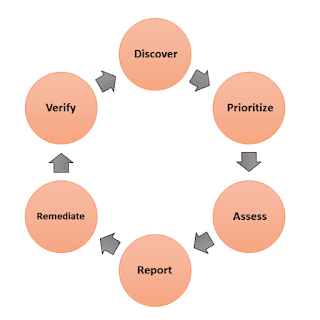
Life Cycle of Vulnerability Management
1. Discover
This step involves the examination of operating systems, web services, hardware, web applications, and existing security patches to discover new vulnerabilities in the computer system.
2. Prioritize
After the discovery of vulnerabilities, these are prioritized based on their nature which is informational, low, medium, high, and critical. The critical vulnerabilities should be dealt with first in the order of precedence.
3. Assess
Now, assess all the vulnerabilities based on their severity. For example, low-risk vulnerabilities that affect one or two system does not require some level of urgency as high-risk vulnerability that affects all laptops and desktops.
4. Report
After Assessing each vulnerability, create a security plan for the computer system according to the risk and their level of importance. Document the steps that will be taken to remediate all known vulnerabilities.
5. Remediate
This is the most crucial step of the life cycle of vulnerability assessment. In this step, we take actions to fix the vulnerabilities like updating the hardware and software, applying security patches, updating configuration, etc.
6. Verify
This is the final step in which all the remediation measures taken are verified to eliminate the chances of errors. This step may take some time as verification should be done on all systems and ecosystems.