Structure of Hair and its Characteristics
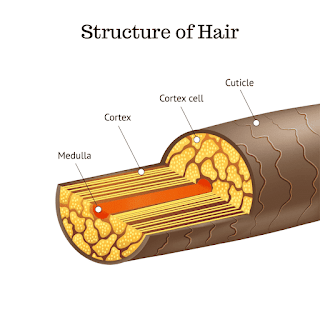
Structure of Hair
1. Cuticle
The cuticle is the outermost translucent layer of the shaft of the human hair. It is smooth and flat and acts as a protective layer for the hair. The cuticle looks like fish scales or roof tiles. It is an important part of the hair that determines the hair species.
2. Cortex
The cortex is the middle layer of the hair which is made up of long thin cells. It consists of long keratin filaments that are held together by disulfide and hydrogen bonds. It also contains the natural hair coloring material (pigment) which is called melanin. It provides stability, elasticity, and a unique color to the hair.
3. Medulla
The medulla is the central core of the hair which is composed of soft keratin protein which may be either absent or present. If present, it may be fragmental, interrupted, or continuous. It is absent in some species and does not determine the species of hair.
Characteristics of hair to determine the species, race, sex, and site
1. Color
The color of the hair sample depends upon the pigment, surface, transparency, and reflectivity. Color is the most useful characteristic of the composition.
2. Structure
The structural parameters of hair like diameter, medullation, cross-section, and spatial configuration. The diameter can be calculated and the medullation can be categorized based on various schemes.
3. Treatment
The external treatment done on hair in terms of dye, cut, split, worn, frayed, etc can be easily identified in the lab. For example, a dyed hair sample can be washed and the actual color of the hair can be obtained whereas tears like cut, split, worn, etc can be analyzed under light or stereomicroscope.
4. Medulla
The medulla sometimes helps in differentiating human hair from animal hair. In human hair, the medulla is narrow and in the majority of cases it is absent whereas, in animal hair, it is broad and always present and continuous.