Different Organelles of Animal and Plant Cell
What is Animal Cell?
The animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell having a nucleus at the center that contains the DNA and the cell is covered with a selective membrane called cell or plasma membrane that only allows the passage of some specific materials.
A cell carries out all the processes of the body which include producing energy and storing it, making proteins which are molecules that have roles in metabolism, transportation of other molecules, and DNA replication.
Different organelles of Animal cell and their function
1. Cell/plasma membrane
A cell membrane is a semipermeable selectively permeable membrane that regulates the entry and exit of nutrients, food, and other entities of the cell. It allows only specific material to pass through it. The cell membrane also separates the organelles of the cell from the outside medium. Thus, protecting the cell from its surroundings.
2. Nucleus
The nucleus is present at the center of the cell occupying nearly 10% of the space. A nucleus is the control and administrative center of the cell which regulated the working of other organelles of the cell. The nucleus contains chromatin which is nothing but an unstructured form of DNA. The nucleus also contains other sub-organelles like nucleolus and nucleosomes.
3. Nuclear membrane
It is nothing but a double-membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus. It is also called a nuclear envelope.
4. Lysosome
It is also known as the suicidal bag of the cell which contains some special digestive enzymes which help in the digestion of own cell in case of any damage or attack by a foreign pathogen.
5. Cytoplasm
It is a jelly-like substance that contains all the cell's organelles enclosed within the cell membrane.
6. Golgi-Apparatus
Golgi apparatus works like a post office in the cell which is involved in the manufacturing, storing, packing, and transporting of the particles throughout the cell. It also helps in modifying the lipids and proteins which have been built in the endoplasmic reticulum and prepares them for transport to other locations of the cell.
7. Mitochondria
Mitochondria are rod-shaped organelles that are known as the powerhouse of the cell. They help to convert the oxygen into ATP which provides power to the cell for performing various activities like respiration, reproduction, division, etc.
8. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are tiny organelles composed of neatly 60% of RNA and 40% of proteins. Ribosomes are found in the endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear membrane and they are responsible for the production of protein.
9. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
RER is a type of endoplasmic reticulum which is specialized in protein synthesis. It is mainly formed by cisternae. In RER, Ribosomes occur over the surface.
10. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
SER is a type of endoplasmic reticulum that is specialized in lipids and steroid synthesise. It is mainly formed by vesicles and tubules. In SER, Ribosomes are absent.
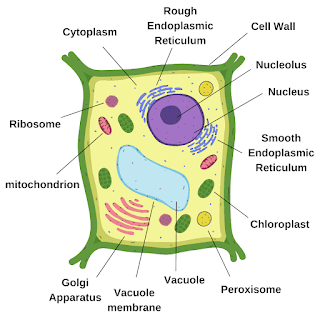
What is Plant Cell?
The plant cell is a type of eukaryotic cell having a nucleus present next to the central vacuole that contains the DNA of the cell. A plant cell is rectangular in shape and also contains a cell wall along with the cell/plasma membrane.
Plant cell contains all the processes of the plant body which includes producing energy and storing it, making proteins which are molecules that have roles in metabolism, transportation of other molecules, and DNA replication.
Here are some key organelles found in cells and their functions:
Different organelles of Plant cell and their function
Note:All organelles are the same as animal cells. Some extra organelles are as follows:
1. Cell Wall
It is a rigid layer that protects the cell from the outside environment and provides structural support to the cell. It is made up of polysaccharides, cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose. It consists of three layers called primary, secondary, and middle layers which help to filter the molecules passing through it.
2. Central Vacuole
The central vacuole occupies around 30% of the cell's volume. It acts as storage space for the cell and sustains pressure against the cell wall. The central vacuole is composed of cell sap, a mixture of salts, enzymes, and various other substances.
3. Vacuole Membrane
The vacuole membrane, also known as the tonoplast, is a specialized membrane found in plant cells that surrounds and encloses the vacuole. The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled organelle that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including storage of water, nutrients, ions, and waste products.
4. Peroxisome
Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles found in plant cells that play a crucial role in various metabolic processes. They are involved in processes such as detoxification, lipid metabolism, and the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
5. Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. They contain a specialized membrane system that facilitates the capture and conversion of light energy into chemical energy.